
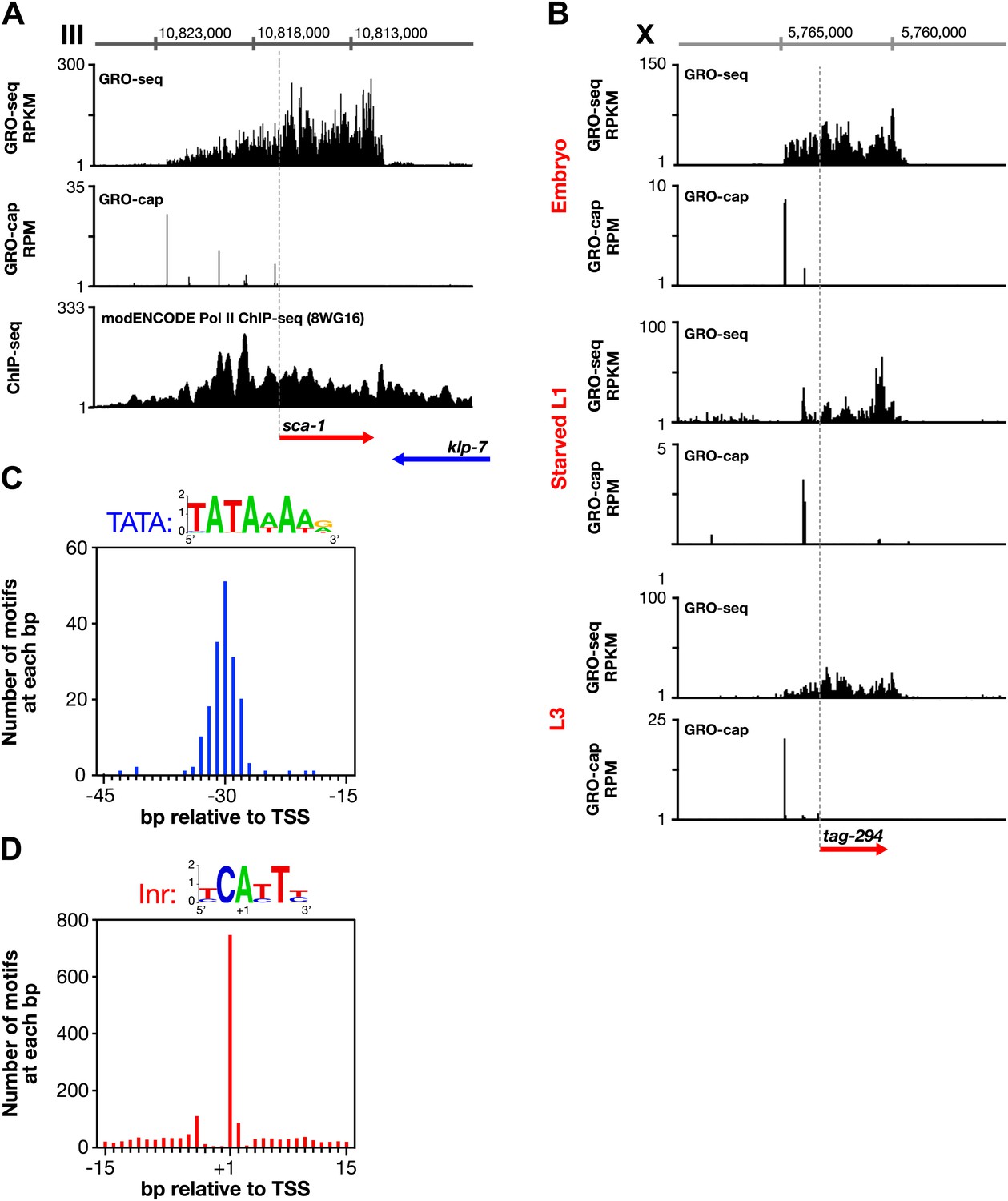
Evidence for ARGONAUTE4-DNA interactions in RNA-directed DNA methylation in plants. DNA-RNA hybrid formation mediates RNAi-directed heterochromatin formation. Nakama, M., Kawakami, K., Kajitani, T., Urano, T. The RNAs of RNA-directed DNA methylation. The Arabidopsis chromatin-modifying nuclear siRNA pathway involves a nucleolar RNA processing center. R-loops induce repressive chromatin marks over mammalian gene terminators. Skourti-Stathaki, K., Kamieniarz-Gdula, K. Human senataxin resolves RNA/DNA hybrids formed at transcriptional pause sites to promote Xrn2-dependent termination. Divergent transcription: a driving force for new gene origination? Cell 155, 990–996 (2013). The determinants of directionality in transcriptional initiation. DNA topoisomerase 1 prevents R-loop accumulation to modulate auxin-regulated root development in rice. RNA-Directed DNA methylation: the evolution of a complex epigenetic pathway in flowering plants. Genome-wide DNA hypomethylation and RNA:DNA hybrid accumulation in Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome. Nascent RNA sequencing reveals distinct features in plant transcription. DREME: motif discovery in transcription factor ChIP-seq data. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. R-loop stabilization represses antisense transcription at the Arabidopsis FLC locus. Sun, Q., Csorba, T., Skourti-Stathaki, K., Proudfoot, N. Prevalent, dynamic, and conserved R-loop structures associate with specific epigenomic signatures in mammals. S1-DRIP-seq identifies high expression and polyA tracts as major contributors to R-loop formation. RNA:DNA hybrids in the human genome have distinctive nucleotide characteristics, chromatin composition, and transcriptional relationships. Genome-wide distribution of RNA-DNA hybrids identifies RNase H targets in tRNA genes, retrotransposons and mitochondria. Genome-wide profiling of yeast DNA:RNA hybrid prone sites with DRIP-chip. GC skew at the 5' and 3' ends of human genes links R-loop formation to epigenetic regulation and transcription termination.
R-loop formation is a distinctive characteristic of unmethylated human CpG island promoters. Characterization of monoclonal antibody to DNA.RNA and its application to immunodetection of hybrids. Transcription as a threat to genome integrity. Nascent connections: R-loops and chromatin patterning. R loops: new modulators of genome dynamics and function. A double-edged sword: R loops as threats to genome integrity and powerful regulators of gene expression. Recognition of the unique structure of DNA:RNA hybrids. Our analyses indicate that R-loops are common features in the Arabidopsis genome and suggest that the R-loops play diverse roles in genome organization and gene regulation, thereby providing insights into plant nuclear genome formation and function. Furthermore, R-loops are negatively correlated with CG DNA hypermethylation, and are prevalent in regions with multiple chromatin modifications, showing strong correlations with the activated and repressed gene loci.
R-loops are strongly enriched in gene promoters and gene bodies, and are highly associated with noncoding RNA and repetitive genomic regions. We found that Arabidopsis R-loops are enriched by both AT and GC skews, and are formed in the sense and antisense orientations. When applied in Arabidopsis, ssDRIP-seq exhibits high efficiency, low bias and strand specificity. Here, we report ssDRIP-seq, a single-strand DNA ligation-based library preparation technique for genome-wide identification of R-loops. R-loops are functional structures in chromatin comprising one single-stranded DNA and a DNA:RNA hybrid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
